Z Decaying to quarks
-
The electron and positron beams collide in the
centre of the detector
-
A Z particle is produced (at rest)
-
The Z particle immediately decays into two quarks
-
Quarks cannot exist as single particles in nature.
Instead they 'dress themselves' as either baryons (3 quarks bound together)
or mesons (a quark and an anti-quark bound together).
-
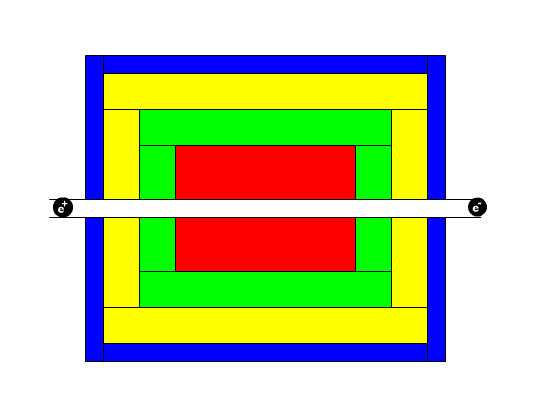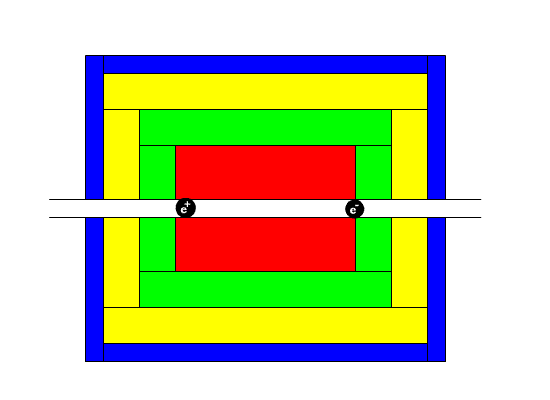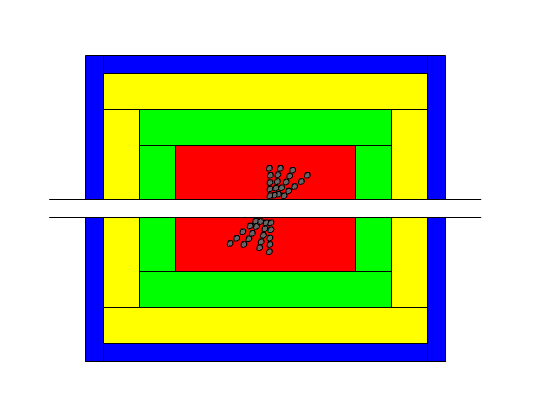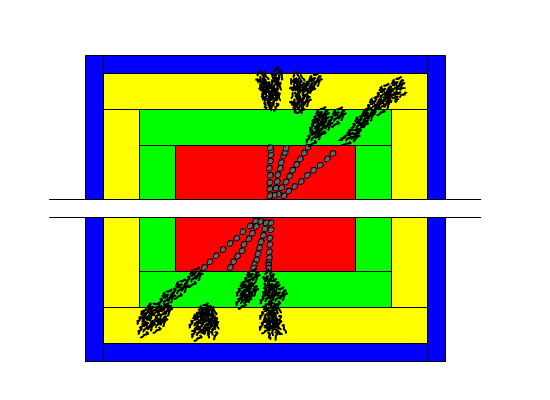
The baryons and mesons are seen in the detector
as charged tracks in the tracking chamber (red)
-
The baryons and mesons loose most of their energy
in the hadronic calorimeter (yellow), rather than the electromagnetic calorimeter
(green)
BACK

