When you clicked on the tracks on the previous page, you probably noticed numerical information on each particle appearing in the boxes underneath the detector.
The upper right box shows the momentum in SI units, ie kg m/s. The SI units of energy, mass and momentum are too large to be convenient in particle physics, so a new unit of measurement is introduced - the electronvolt.
One electronvolt is defined as the change in potential energy when one electron is moved across a potential difference of 1 V, i.e.
In particle physics, it is convenient to measure energies in eV. Also, one can measure masses in units of eV/c2 and momenta in units of eV/c :
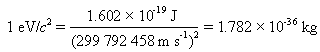
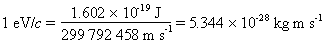
In fact, the momenta are quoted in GeV/c.
1 GeV = 1 gigaelectronvolt = 109 eV
| Previous | Next |